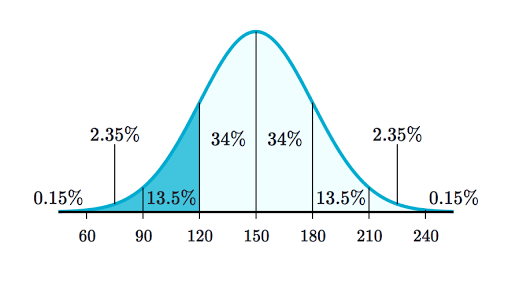
This means there is a 68 probability of randomly selecting a score between -1 and 1 standard deviations from the mean. D P d t k P 1 P M frac dP dtkPleft 1-frac P Mright d t d P k P 1 M P where M M M is the carrying capacity of the population.
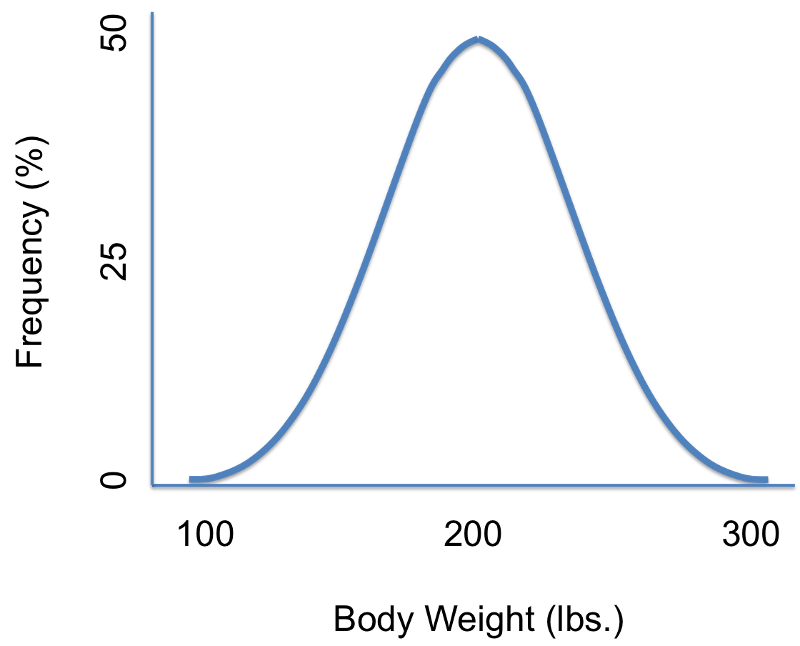
The Normal Distribution A Probability Model For A Continuous Outcome
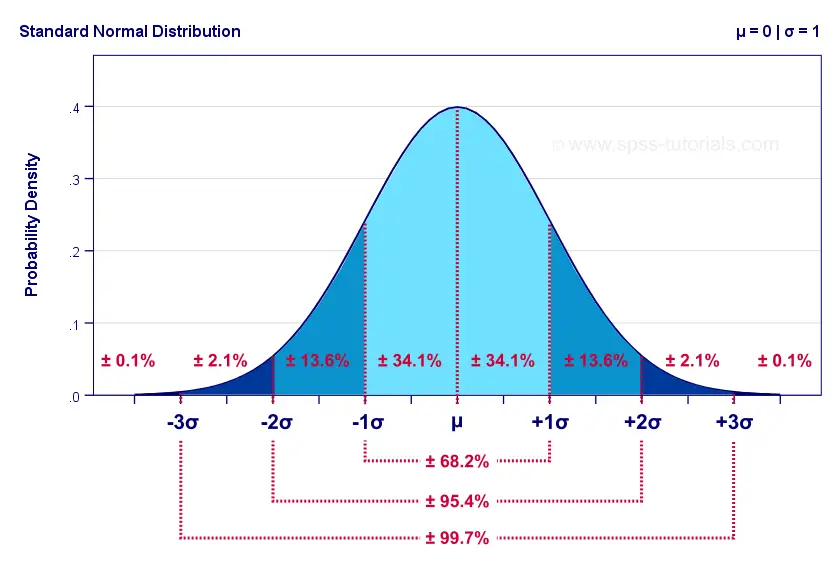
For any probability distribution the total area under the curve is 1.
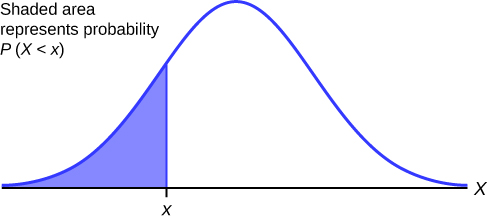
. A Normal Population with known I This case is not common in practice. Many important statistical procedures can be carried out using only one type of probability density curve called a normal curve. Check out our sampling blog to learn more about why good sampling is important.
True TRUE OR FALSE. Sixty-five percent answered the economy. The probability is about 00475.
A population is a set of existing units. For the normal distribution we know that the mean is equal to median so half 50 of the area under the curve is above the mean and half is below so P BMI 29050. To find the shaded area you take away 0937 from 1 which is the total area under the curve.
How Probability Distributions Work Perhaps the most common probability distribution is the normal distribution or bell curve although several distributions exist that are commonly used. In other words the properties of the normal curve can be used to estimate the probability of a case or score with reasonable accuracy. For a proportion the appropriate standard deviation is pq n p q n.
An example of a qualitative variable is the mileage of a car. The probability is about 00475. It uses randomization to guarantee that every unit in the population has a non-zero known probability of being included in the sample.
STA2023 Lecture Notes 1 71 72 The Standard Normal Curve Use a probability density curve to describe a population The following figure presents a relative frequency histogram for the particulate emissions of a sample of 65 vehicles. Probability defined as proportion fraction or percent of all possible outcomes Random Sampling To make inferences about population from sample using probability theory select elements by this Each element in population has an EQUAL and KNOWN chance of being selected Probabilities must stay constant from one selection to next replacement. For a mean when the population standard deviation is known the appropriate standard deviation that we use is σ n σ n.
The second histogram looks smooth and could be approximated by a curve. The empirical rule allows researchers to calculate the probability of randomly obtaining a score from a normal distribution. This formula is similar to the error bound formula for a mean except that the appropriate standard deviation is different.
68 of data falls within the first standard deviation from the mean. A random sample is selected so that every element in the population has the same chance of being included in the sample. The output of a probability mass function is a probability whereas the area under the curve produced.
Examples include the height of an adult picked at random from a population or the amount of time that a taxi driver has to wait before their next job. Population estimates are often derived from a sample because its rare that we can measure the entire population. True TRUE OR FALSE.
Lets try an example with a small population that has normal growth. If the sample represents the population the normal curve is a useful estimation tool. The probability distribution is a type of statistical calculation used by traders to demonstrate the likelihood that a particular variable will.
When we use a probability function to describe a discrete probability distribution we. This is the probability of SAT scores being 1380 or less 937 and its the area under the curve left of the shaded area. We will use it to illustrate basic principles of test procedure design I Let X 1X n be a sample size n from the normal population.
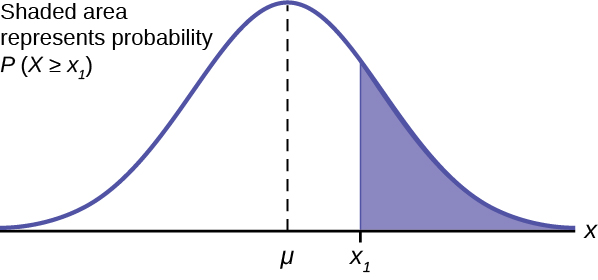
So we want the probability that the z -score is greater than or equal to 167. Consequently if we select a man at random from this population and ask what is the probability his BMI. See the answer 3-5 sentences please.
The null value of the mean is usually denoted 0 and we consider testing either of the three possible alternatives 0 0 and 6 0. Probability in normal density curves Our mission is to provide a free world-class education to anyone anywhere. Time series data are data collected at the same time period.
Provide an explanation that demonstrates your understanding of probability and the normal symmetrical distribution curve. This problem has been solved. To model population growth and account for carrying capacity and its effect on population we have to use the equation.
Probability of x 1380 1 0937 0063 That means it is likely that only 63 of SAT scores in your sample exceed 1380. Probability sampling leads to higher quality findings because it provides an unbiased representation of the population. The relationship between inferential statistics and probability As we learned earlier gathering information about an entire population often costs too much or is virtually impossible.
Khan Academy is a 501c3 nonprofit organization. Probability is the underlying concept of inferential statistics and forms a direct link between samples and the population that they come from. A poll of 1200 voters asked what the most significant issue was in the upcoming election.
When we use terms like near far likely close and unlikely close to describe sample and population scores what are we talking about. We are interested in the population proportion of voters who feel the economy is the most important. Use a normal curve to describe a normal population Normal Curves Probability density curves comes in many varieties depending on the characteristics of the populations they represent.
If it is true that 10 of the population of 18- to 24-year-olds are enrolled at a community college then it is unusual to see a random sample of 100 with 15 or more enrolled. Use the following information to answer the next five exercises. False TRUE OR FALSE.

Using The Normal Distribution Introductory Statistics
Using The Normal Distribution Introductory Business Statistics
0 Comments